Hello Everyone,
Today i am going to share components, tools and processes required to implement ALM.
Lets gets started.
Environments: They serve as a container for all apps, its to store, manage and share your business data.
They serve as a container to separate apps that might have different roles, security requirement, or target audiences.
Note: Each environment will have one Microsoft Dataverse Database.
Also when we create a new environment, choose the Dynamics 365 apps like Dynamics 365 Sales, Service, which are required now or in future. If you dont want them then not to install which are not required otherwise they will create dependency issues when we deploy solutions between ennvironments.
Environments used in ALM:
With the Power Platform admin center, you can create the environments:
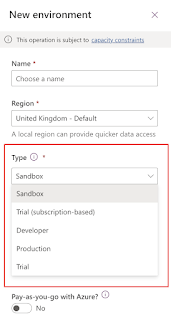
Environments types:
Sandbox: Its a development environment, in other terms non production environment.
Production: Its a LIVE environment for your organisation, where business users will access day to day activities for sales, customer service, marketing, field service.
Developer: Power App Develper Plan gives access to Power Apps premium functionality, Dataverse, Power Automate for individual use. its a single user environment and its not used to run or share production apps.
Default: Its a default environment created for each tenant and shared by all users in that tenant.
Who should have access to these environments, Microsoft Power Platform Provides environment level admin roles to perform tasks.
Development environment will have App Makers and developers have access to it.
Test environment: Testing users and admins will have access to it.
Production environment: Admins and app user and they should have access privileges to perform the tasks.
Default: By default every users will have create and edit apps permissions, so create an environment for development activities and testing and production and provide appropriate permissions for them.
Solutions: Solutions are used to transfer apps and components from one environment to another, they only contain metadata and certain entities with configuration data.
Source Control:
Source control otherwise known as Version Control, when you makes any changes to the solution and deploy to other test or production environment, those changes by multiple users and it is maintained through source control to revert back to previous state if something is wrong.
Source Control helps businesses to achieve healthy ALM because the assests maintained in the source control system are single source of truth or otherwise a single point of access and modification for your solutions.
Source control process using a solution:
Two main paths we can use.
1. Export the unmanaged solution and place it as unpacked in a source control. so the build process imports the packaged solution as unmanaged into a temporary build environment(sandbox environment). then export the solution as managed and store it as a build artifact in your source control system.
2. Export the solution as unmanaged and also export the solution as managed and place both in the source control system. Although this method doesn’t require a build environment, it does require maintaining two copies of all components(one copy of all unmanaged components from the unmanaged solution and one copy of all managed components from the manage solution.
Automation:
Automation is a key part of the application lifecycle that improves the productivity, reliability, quality and efficiency of ALM. Automation tools and tasks are used to validate, export, pack, unpack and export solutions in addition to creating and resetting sandbox environments.
How the Source control being used by your development team
Consider how your development team will be work together as a team to build the project.
some tools and workflows – such as those provided in GIT, GITHUB, and Azure DevOps were designed for the express purpose of improving communication and software quality.
Note: Working with configurations in a solution system can create challenges for team development.
Organisations must orchestrate changes from multiple developers to avoid merge conflicts as much as possible, because source control systems have limitations on how merges occur.
Recommendation: Avoid multiple people make changes to complex components, such as forms, canvas apps at the same time.
Continuous integration and deployment:
You can use any source control system and build a pipeline to start with for continuous integration and continuous deployment(CI/CD).
We are discussing about the Azure DevOps, Github.
Github is a development platform used by millions of developers.
Azure DevOps provides developers services to support teams to plan work, collaborate on code development, and build and deploy applications.
You need the following:
1. A GitHub account, where you can create a repository
2. An Azure DevOps organisation
Licensing:
In order to use Power Platform, Power Apps, Power Automate, users will require a license such as per user or per app license or Dynamics 365 app license.
ALM Considerations:
When you consider ALM as an integral part of building apps on Microsoft Power Platform, it can drastically improve speed, reliability and user experience of the app. it also ensures that multiple developers writing code and citizen developers, can jointly contribute to the application being built.
I hope this helps
Malla Reddy(@UK365GUY)
#365blogpostsin365days